NewsInformation Center
Oxygen Index Test for Electrical and Electronics Components
2023/07/07
The Oxygen Index (OI) test is also applicable for evaluating the flammability characteristics of electrical and electronics components. The OI test measures the minimum concentration of oxygen required to sustain combustion of a material in a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gases. It provides an indication of the material's resistance to burning in an oxygen-rich environment. Here is a general outline of the Oxygen Index test procedure for electrical and electronics components:
1. Sample Preparation:
a. Select representative samples of the electrical or electronics components to be tested.
b. Ensure that the samples are of appropriate size and shape for testing. The dimensions may vary depending on the specific requirements and standards.
c. If necessary, remove any protective coatings or surface treatments from the samples, ensuring that the exposed material is representative of the component.
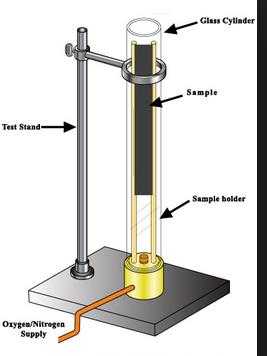
2. Test Apparatus Setup:
a. Set up the Oxygen Index test apparatus according to the specific standard or method being followed.
b. Ensure that the apparatus is clean and free from any contaminants that could affect the test results.
c. Install the sample holder or specimen support system in the apparatus, ensuring proper alignment and secure positioning of the components.
3. Preconditioning:
a. Condition the samples in a controlled environment for a specified period, if required by the test standard. This step helps ensure consistent moisture content and temperature of the samples.
4. Test Procedure:
a. Place the conditioned sample into the sample holder or specimen support system.
b. Adjust the oxygen and nitrogen flow rates to achieve the desired oxygen concentration, typically between 21% and 100%.
c. Ignite the exposed end of the sample using a suitable ignition source, such as a pilot flame or electrical spark.
d. Observe the sample during the test and record relevant data, including the time taken for ignition, the burning rate, and any other observations specified in the test standard.
e. Continue the test until the sample either self-extinguishes or burns completely.
5. Calculation and Reporting:
a. Calculate the Oxygen Index (OI) value using the formula specified in the test standard. The OI is typically expressed as a percentage.
b. Report the OI value along with any other relevant test data, such as the test conditions and observations.
It's important to note that the specific details of the Oxygen Index test for electrical and electronics components may vary depending on the applicable standard or method being followed. It is crucial to adhere to the relevant standards and guidelines, ensuring proper safety precautions and accurate testing procedures.
Previous: What does the luggage zipper test generally include?
N e x t : How often should I calibrate the zipper fatigue tester?