
NewsInformation Center
Up to which limit did the limiting oxygen index need in medical applications?
2023/10/13
The design and use of medical devices involves a number of stringent regulations and standards, one of which is the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI), an important measure of a material's flame resistance.
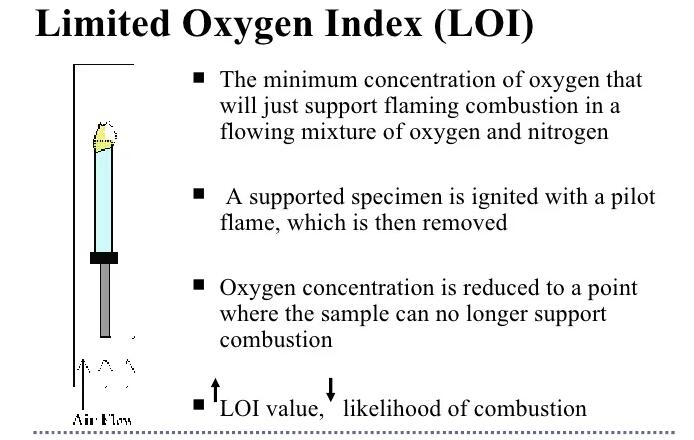

The Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) is a measure of a material's flammability under specific conditions. In this test, a standardised sample is placed in a narrow glass tube and exposed to a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen in a controlled environment. If the sample is able to burn continuously during the test and then stops burning, the fraction of oxygen used (the ratio of oxygen to nitrogen) is defined as the LOI of the material.

The higher the LOI, the better the material's flame retardancy. A low value of LOI indicates that the amount of oxygen required in the gas mixture is low and the sample is prone to burn in low oxygen environments and vice versa.
The selection of materials for medical devices needs to be done with care, taking into account the specificities and safety requirements in the medical environment. In many cases, the LOI is usually higher for various plastics and other combustible materials used in medical devices. This specific value, however, varies by region, type of device and application scenario.
For example, regulations in some countries or regions may set higher LOI requirements for plastic materials used in specific parts of the equipment used (e.g., oxygen supply equipment). Generally, for these applications, the LOI may need to be higher than 25 or 30, or even higher, in order to provide adequate flame resistance in the event of a fire.
However, like many other medical device standards and regulations, LOI is not the only criterion to consider. Other factors related to flame resistance, such as pyrolytic behaviour and smoke development, are equally important. In addition, other important properties of the material need to be considered, such as mechanical properties, biocompatibility, resistance to chemical agents, and aging resistance.

The following are some of the considerations related to the common limits of limiting oxygen indices for medical applications:
1. Safety and fire protection requirements:
Medical devices and materials often need to meet stringent safety and fire protection requirements to safeguard patients and healthcare workers. In high-risk environments or where there is contact with flammable substances, the requirements for the flame resistance of the material may be even more stringent. In such cases, it is often necessary to select materials with a high limiting oxygen index.
2. International and national standards:
Different countries and regions may have their own standards and regulations governing the use of medical devices and materials. These standards and regulations may specify specific limiting oxygen index limits to ensure that the materials used meet local safety requirements. For example, in the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may provide guidelines but does not specify limiting oxygen index limits.

3. Recommendations from industry associations and organisations:
Medical industry associations and organisations often issue guidelines and recommendations to ensure the safety and compliance of medical devices and materials. These guidelines may provide recommended limits or suggested ranges for limiting oxygen indices to help develop appropriate choices.
In determining specific limits for limiting oxygen indices in medical applications, it is important to consider the safety needs of the particular application, relevant regional regulations and standards, and recommendations from industry associations and organisations. It is therefore recommended that when selecting materials and designing for an application, professionals, suppliers and relevant organisations are worked with and consulted on local regulations, standards and expert advice to ensure that the materials selected meet the appropriate requirements and safety standards. This will ensure that the materials used in medical applications have the right performance and safety in terms of fire risk.
Overall, the selection and application of materials for medical devices requires finding the right balance between meeting the requirements of safety standards and the specific functional needs of the device. As a result, medical device manufacturers need to conduct thorough evaluation and testing during the product development process, including an assessment of the material's LOI, to ensure compliance with all relevant standards and regulations.
A final important point is that the various regulations and standards in the medical industry are constantly changing and updating. As scientific research progresses and new technologies emerge, LOIs and other relevant requirements are further developed and optimised. This provides manufacturers with the opportunity to continually improve the performance and safety of their products, as well as provide patients with safer and more reliable medical devices.
Previous: What is the difference between ISO 6892 and ASTM E8?
N e x t : How to Safely Operate Your Taber Linear Abraser Model 5750?



