Search keywords:
product name, product type, model number,
test method, manufacturer, technique, application
Thermal Radiation Performance Tester(RPP)
BACKStandards:
NFPA 1971:Standard on Protective Ensembles for Structural Fire Fighting and Proximity Fire Fighting NFPA 2112:Standard on Flame-Resistant Garments for Protection of Industrial Personnel Against Flash Fire BS EN ISO 6942:Protective clothing — Protection against heat and fire — Method of test: Evaluation of materials and material assemblies when exposed to a source of radiant heat EN 366:Protective clothing — Protection against heat and fire — Method of test: Determination of resistance to molten metal splash ASTM F2702:Standard Test Method for Determining the Heat Transfer Through Materials Used in Protective Clothing Using a Hot Surface ASTM F1939:Standard Test Method for Radiant Heat Resistance of Flame Resistant Clothing Materials With Continuous Heating
Applications:
Outdoor Sports Gear: Evaluating the waterproof breathability and thermal balance of fabrics for jackets, ski suits, and mountaineering apparel.
Specialized Protective Clothing: Testing thermal protection and moisture-wicking performance of firefighting suits, military combat uniforms, and medical protective garments.
High-Performance Fabrics: Evaluating multilayer composite materials for extreme environments like spacesuits and deep-sea diving suits.
Bedding & Interiors: Monitoring thermal resistance properties of sleeping bags, carpets, and automotive seat materials to enhance comfort at home and on the go.
Membrane Material Research: Assisting R&D personnel in testing technical specifications of moisture-permeable components like microporous membranes and non-porous hydrophilic films.
Product Information:
Thermal protective clothing and some fire-retardant properties of the material refers that human body carry out security protection who work under high temperature conditions, so as to avoid the human body's high temperature injury. In theory, there are three forms of heat damage to the human body:
thermal convection; B. heat transfer; C. thermal radiation;
In general, the practical application is more than the above two or three kinds of mixing effect. So the thermal protection should be used for different purposes and use of the environment to highlight its certain thermal protection performance.
I. Thermal Radiation Protection Performance Test Method (RPP Test) Radiant Protective Performance;
II. Thermal Radiation and Heat Convection Mixing Protective Performance Test Method (TPP Test) Thermal Protective Performance;
The RPP test is mainly used to determine the radiant thermal protection performance of thermal protective clothing. Since thermal radiation is one of the main heat transfer forms that cause thermal damage. The method can better test and evaluate the thermal protection performance of thermal protective clothing from one aspect, and has been widely used in the field of forest fire.
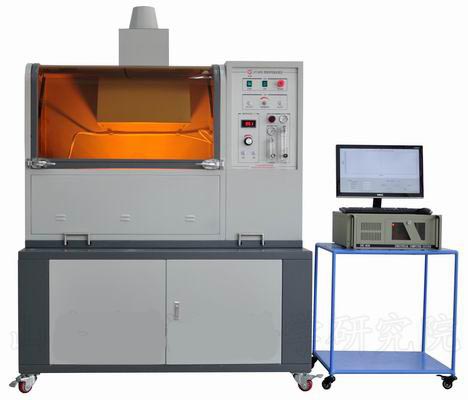

Feature
◆ Evaluation of flame retardant properties of flame retardant materials
◆ Detect abnormalities and reduce accidents
◆ Calculate the RPP value
◆ Evaluate thermal protection performance
◆ Improve job safety
◆ Improve the quality control system
Technical Parameters
| Items | Parameters |
| Heating power | 6.5Kw/220V/50Hz |
| Heating length | 178mm, diameter 8mm |
| Heat flux density | 10Kw/m2-80Kw/m2 |
| Radiation source temperature control | -1200℃±5℃ |
| Thermal radiation source temperature sensor | Thermocouple (0 ℃ -1600 ℃) |
| Calorimeter heat capacity | 480.937J/K |
| Heating area | 50mm2×50mm2 |
| Calorimeter temperature range | -80℃ |
| Test environment |
Between 15 ℃ -35 ℃ ,the room without air circulation |
Accessories
(1) Porous Test Plate Assembly
(2) Preheating Plate with Protective Ring
(3) High-Precision Water Supply System
(4) Semipermeable Membrane (for Wet Resistance Testing)
(5) Ambient Temperature and Humidity Sensor
(6) Computer Data Acquisition Software System
Test Procedures
System Preheating: Power on the instrument, set the test plate temperature (e.g., 35°C) and ambient chamber temperature/humidity, allowing the system to reach stable equilibrium.
Thermal Resistance Test (Dry Test): Cover the test plate with a dry sample and measure the constant heat flux required to maintain the temperature difference under water-free conditions.
Wet Resistance Test (Wet Test): Cover the test plate with a semi-permeable membrane simulating skin and inject distilled water.
Sample Installation: Place the test sample flat over the semi-permeable membrane and activate the parallel airflow system.
Data Acquisition: After the system re-establishes dynamic equilibrium, record the heat consumed by water vapor evaporation via software.
Calculation Results: Software automatically subtracts no-load resistance, outputting the material's final thermal resistance ($R_{ct}$) and wet resistance ($R_{et}$) values.
Maintenance Information
Water Circuit Cleaning: Wet resistance testing must use medical-grade distilled water or deionized water. Tap water is strictly prohibited to prevent scaling and clogging of the porous plate.
Sensor Protection: Keep the gap between the protective ring and the test plate edge clean to prevent fiber debris from affecting airflow distribution.
Calibration Recommendation: Periodically verify the system's heat flux response using a standard calibration plate.
Long-Term Storage: If the moisture resistance function remains unused for extended periods, drain the water supply lines and keep the test plate surface dry.
Conclusion
This thermal protection performance testing system provides a comprehensive and reliable means to evaluate the resistance of protective clothing materials against radiant heat, convective heat, and their combined effects. By accurately measuring RPP and TPP values in accordance with multiple international standards, it supports the assessment of flame-retardant properties, thermal safety, and material reliability under high-temperature conditions. The system is widely applicable to protective clothing, high-performance fabrics, and interior materials, helping improve safety performance, reduce heat-related risks, and enhance quality control and product development for thermal protective applications.
FAQ
1. What is this product?
Answer: It is a precision analytical instrument that physically simulates human skin's heat dissipation and moisture production processes to specifically measure the thermal resistance and moisture resistance values of fabrics.
2. What is this product used for?
A: It quantitatively evaluates a fabric's thermal efficiency and moisture-permeable comfort, serving as the “certificate of identity” for high-end functional fabrics entering the market.
3. How does this product work?
A: A thermostatically controlled heating plate maintains a specific temperature to measure heat loss through the fabric. The moisture resistance test additionally measures the material's resistance to moisture vapor transmission via evaporation.
4. Why is this product important?
Answer: Insufficient moisture resistance in outdoor apparel leads to overheating, chills, or hypothermia; inadequate thermal resistance fails to provide warmth. This instrument provides scientific validation for ensuring garment performance meets standards.
5. Which industries benefit from this product?
Answer: It is widely used in textile research institutes, third-party testing agencies, R&D centers of premium sportswear brands, and manufacturers of specialized protective workwear.