
NewsInformation Center
How To Produce Good Meltblown Nonwoven Masks
2020/06/03
The surgical masks, which cover the nose and mouth, are often made from a flimsy material and aren’t fitted to the face. In other words, spaces and gaps can form around the cheeks and edges of the mouth, making it easy for air to move in and out.
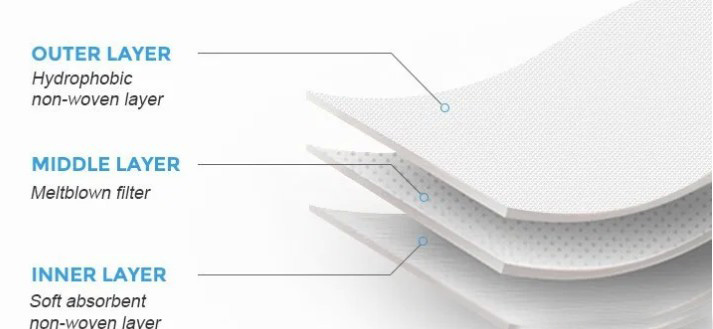

This 3 ply material is made up from a melt-blown material placed between non-woven fabric. The melt-blown material acts as the filter that stops microbes from entering or exiting the mask.The meltblown nonwoven, the core material of the mask, determines to a large extent whether the masks made are qualified.
Good meltblown nonwoven masks are generally not too bad, meltblown nonwoven test reports generally do breathing resistance tests, filtration efficiency test, microbial test, and other three items. If you want to produce a mask, you should first test the meltblown nonwoven to see if it is qualified, so that the meltblown nonwoven does not fail, resulting in the production of the mask is not qualified then it will be a loss.
Most surgical masks feature pleats or folds. Commonly, 3 pleats are used allowing the user to expand the mask so it covers the area from the nose to the chin. Inner and outer materials, mostly polypropylene spunbond nonwoven materials, the particle filtration efficiency of which is limited. The middle layer to play a particle filtering role with the electret polypropylene meltblown nonwoven materials, the material can use electrostatic adsorption of particles, thus greatly improving the filtration efficiency.
The filtration of particulate matter by filtration materials mainly has the effect of gravity settlement, interception, inertial collision, diffusion, electrostatic adsorption, etc. Under the joint action of various filtration mechanisms, there is a minimum value of filtration efficiency for particulate matter with an aerodynamic particle size around 0.3µm, which is commonly known as the most easily penetrating particle size (MPPS).
MPPS is determined from flat sheet testing of the filter medium in accordance with EN 1822-3, then the filter is tested at this predetermined particle size. The efficiency is determined by particle number counting. If the aerosol is quasi-monodispersed, the aerosol generated has to have a particle size near MPPS. If the aerosol is polydispersed its fractional efficiency counting is done to determine MPPS.
Previous: what is fabric pilling ?
N e x t : ASTM F2100 :Five Performance Requirements For Medical Face Masks



